Ransomware Attacks – Anatomy and Likelihood
Why You Should Act Now!

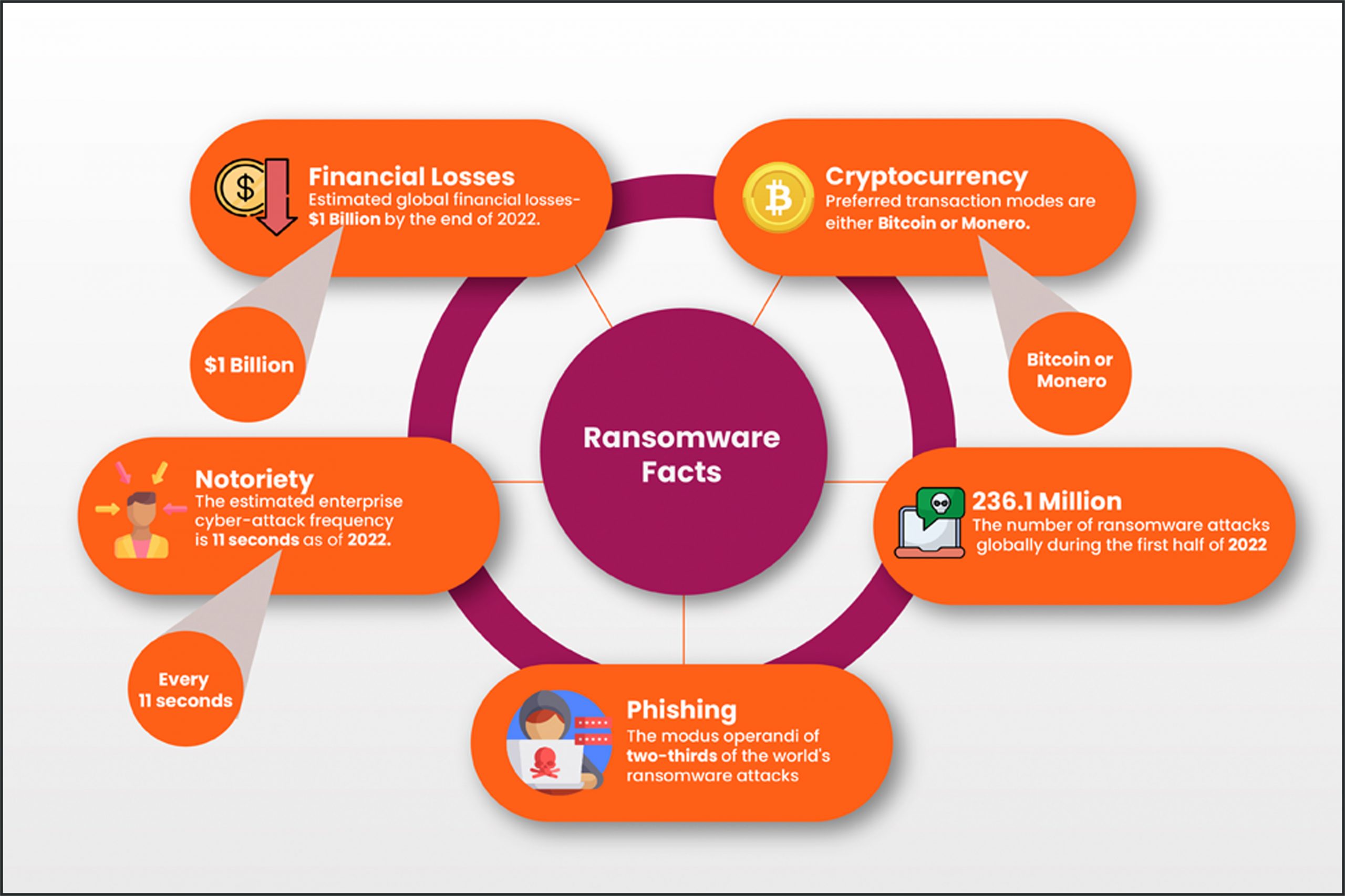
The Internet Crime Report generated by the FBI’s Internet Complaint Crime Center (IC3) has reported that ransomware attacks have resulted in losses to the tune of $49 million globally in 2021 alone. The annual losses are estimated to peak further and reach a whopping $1 Billion globally by the end of 2022. The modus operandi of two-thirds of these attacks has been through phishing emails. The cyber-attack form has evolved from many small phishing campaigns to fewer but more impactful attacks on large corporations recently.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a form of malware (an abbreviation of “malicious software”) created to block users from accessing enterprise resources such as endpoints and servers. The program usually encrypts data sources, making them indecipherable, and demands businesses ransom by holding their data hostage. Globally, several large corporations have been at the receiving end of ransomware attacks and have ended up paying a ransom in return for access to their data. Smaller businesses have proved to be no less of a target.
The rising number of ransomware incidents has undoubtedly created a sense of awareness of the threat among enterprise owners, but many are yet to zero in on an effective ransomware mitigation strategy. Of late, BluVault has emerged as an effective ransomware protection and recovery measure for endpoint and Microsoft 365 data. A deep dive into the solution, built on the foundation of a patented data protection methodology, will help one understand how BluVault approaches ransomware and gets an affected enterprise to quickly recover.
Parablu’s BluVault for Ransomware Protection
BluVault is a cost-effective, robust data resiliency solution that is designed to help businesses recover from a ransomware attack without having to negotiate with the attacker.
- Automatic, Policy-driven Backups
BluVault’s policy-driven backups help you define the files/folders to be archived and the frequency of backups – making an enterprise ransomware-prepared. It can be seamlessly integrated with existing OneDrive or Google Drive subscriptions and incurs no additional storage costs.
- Data Immutability
BluVault does not just encrypt critical data to prevent tampering, it also creates a virtual airgap to the storage target – ensuring that ransomware cannot infect and corrupt the backups.
- Curated Recovery
BluVault can identify and restore only those files that were deleted by ransomware while filtering out any corrupted files that may have bled into the backup. The result is low-impact and business continuity for end users.
- File Quarantining
The built-in file and device quarantining capabilities help incident management teams easily isolate “patient-zero” systems and the malicious payload from being recovered as part of restore operations.
- Data Management Reports
BluVault is equipped with an ML (Machine Learning) engine that helps detect ransomware-corrupted files. This helps in early detection and prevents such files from getting restored.
Comprehensive data management reports offer IT admins insights that help detect ransomware attacks early.
Anatomy of a Ransomware
To prevent a ransomware attack and formulate an effective incident response, it is important to trace its origin and understand how it spreads. A comprehensive understanding of the anatomy of a ransomware attack will help harness a data protection solution better.

- Campaign
The attackers offer bait in the form of a phishing email with attachments or website links, which when clicked or downloaded install malicious software in potential target system/s.
- Infection
Also known as instantiation, in this stage, the malicious code establishes a communication line between the attacker and the victim(s). Through the established communication line, the malicious software may also infiltrate other systems across the enterprise network. The attacker typically ensures the infection stays dormant for many days and announces the threat when the time seems right.
Another popular infection vector is the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), which could be leveraged if the attacker is aware of the employee’s login credentials. The masquerading agent can gain access to the target enterprise network, download, and execute the malware on the target system using this approach.
- Staging
To ensure a successful attack, the ransomware moves across folders and identifies critical information such as proxy settings, user privileges, local configuration files, and registry keys. Additionally, the ransomware also runs commands to disable recovery mode and delete copies of the original files. Some ransomware variants create private/public encrypted keys and append them at the end of every file’s byte stream. The malware scans the last few bytes of these files when it needs to carry out the decryption. The private keys are securely stored in the Command and Control server – leveraged by attackers to establish control over target endpoints or servers.
- Encryption
Ransomware encrypts critical data sources ranging from the master boot record of the file system to data backups and does its utmost to ensure no recovery is possible. It has been observed that the target organization’s data repositories are scanned for directories or files either named in the date format (bigdata20220907.bak) or containing a .bak extension. Such files are infected first, and eventually, the attack extends to other data formats stored in the system.
- Ransom Demand
After the target system or network has been encrypted beyond recovery, the attackers demand a ransom for the decryption, which they insist must be transacted through digital currency options such as Bitcoin or Monero, which are untraceable.
Why You Should Care

“While many organizations plan for a ransomware defense, few have a recovery strategy to deal with a situation where they get attacked. It is critically important to understand the adverse impact of such a cyber-attack on the company.”
“Various surveys reveal that there is a ransomware attack somewhere in the world every 11 seconds.”
- Business Loss
Ransomware infiltration results in extended downtimes, sometimes spanning months. A recent infamous example was the attack on Brazil-based meat processing company, JBS, which led to a temporary shutdown of the company’s Australia, Canada, and U.S. facilities. Business operations could resume only after the ransom was paid by the organization. Nvidia, America’s largest microchip manufacturer, fell prey to a ransomware attack carried out by the hacker group Lapsus$ in 2022. The incident resulted in data worth 1TB being stolen for ransom, which included proprietary source code, credentials, and a 2-day downtime.
- Ransom Payment
A difficult decision for an enterprise is whether to pay a ransom to recover critical data. While cybersecurity experts advise against the move, businesses take the plunge to get back critical information with no guarantee that critical data won’t be held hostage once again.
- Reputation Damage
Ransomware attacks result in irreversible reputation damage to a firm. Not only does the news of the attack portray the company in a bad light but could also result in customer retention issues since confidential data is compromised.
- Regulatory Fines
Loss of data due to a ransomware attack could also result in heavy penalties under regulations such as the GDPR.
Call to Action! How to Keep Ransomware at Bay
Security measures such as Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) software alone will not be sufficient to prevent ransomware attacks. Here are a few best practices that can help prevent the threat and the resultant fallout.
- Increased Employee Awareness
User endpoints are usually the gateway for ransomware attacks and employees must be the first line of defense. Employee awareness training around recognizing phishing emails can prevent instances of malicious file downloads, the resultant downtime, and ransom payments. Education on threat responses and reporting, safe utilization of vulnerable storage devices such as USBs, and secure file sharing can contribute significantly to a company’s ransomware defense mechanism or readiness.
” Employee awareness training around recognizing phishing emails can prevent instances of malicious file downloads, the resultant downtime, and ransom payments.”
- Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication necessitates the utilization of two or more user credentials to access the required files. Multi-factor authentication comprises three aspects, namely knowledge, possession, and inherence. While passwords and answers to personal questions fall under the purview of knowledge-based multi-factor authentication, One Time Passwords (OTP) and fingerprints are examples of possession and inherence, respectively.
- Robust Data Backup Strategy
Implementation of a tamper-proof data backup strategy that ensures timely archival, as well as data restores, is imperative. A future-proof backup strategy offers not just protection but can also reduce cyber insurance premiums and significantly reduces the likelihood of a regulatory fallout in cases of ransomware attacks.
- Principle of Least Privilege
Also known as the Principle of Least Authority (POLA), least privilege is the practice of granting only the bare minimum number of access rights to a limited, authorized set of users. Minimal access permissions prevent instances of breaches by users.
- Cybersecurity Insurance
Cyber insurance covers an enterprise during a breach of critical customer data and also helps organizations stay regulatorily compliant.
- Secure Managed File Transfer
Conventional file transfer protocols such as SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) encrypt the data only in transit, whereas modern Managed File Transfer (MFT) solutions protect data at rest too.
- Central Data Management
Centralized console-based data management helps administrators gain better visibility of enterprise data, define data-sharing policies, and adhere to compliance requirements.
- Incident Preparedness
Forming an incident response team, defining a communication plan, and creating a contact list of the required stakeholders including law enforcement and regulators about cyber incidents is vital.
Being equipped with Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery plans are crucial to maintaining operations after a disruption.
- Cyber Drills
A cyber drill activity to spread awareness about ransomware and methods to mitigate the threat across organizational hierarchies go a long way in pre-empting attacks. Helping employees understand how they could individually prevent a threat must be a part of the employee cybersecurity awareness program.
- Never Pay the Ransom
Paying the ransom signals to the attacker that you are vulnerable and don’t have a robust recovery mechanism. Several enterprises in the recent past have paid a ransom only to get attacked a few months later. Government agencies and cybersecurity experts have mandated organizations to refrain from paying a ransom.
Once infected by ransomware, the attacker displays an interface prompting the user to pay the demanded amount. However, many times, even after paying, the enterprise does not receive the decryption keys. In addition, most ransomware attackers insist on cryptocurrency payments that cannot be reversed or traced.
An All-encompassing Data Backup Solution
In summary, it is better to be prepared with a robust cybersecurity program, and defense-in-depth security infrastructure alongside a strong data resiliency solution. This will prevent attacks and in the worst case of a successful attack ensure your data is worthless to the attacker while getting you your data back quickly and continuing to execute your business as usual.
Ransomware attacks trigger downtimes, cause financial losses, and even incur regulatory fines if data protection measures are not implemented. Beyond ransomware protection, BluVault encompasses regulatorily compliant data protection best practices, offers benefits such as Litigation Hold, and incurs no additional storage costs.
Learn more about how BluVault can offer you the best ransomware protection through this demo.
Glossary










