Digital and Information Rights Management –The correct way to share information

A slew of content management challenges has emerged because of digitization. Online copyright infringement instances such as re-distribution of existing content and extracts from different published material being compiled to produce new works are common.
Critical enterprise data shared among a set of users have triggered instances of corruption, malware, and insider attacks. The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021 stated that the global average breach cost rose from $3.86 million to $4.24 million during the year. Several such financial loss instances caused by data vulnerability have resulted in the wide adoption of digital and information rights management.
What is Digital Rights Management?
Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a framework that overcomes the limitations of existing copyright laws by leveraging advanced tools to better protect proprietary data. DRM is commonly adopted to prevent piracy of books, Blu-ray discs, DVDs, and audio files.
DRM helps impose restrictions on the number of times or devices from which certain files can be accessed. Overall, DRM helps prevent unauthorized data redistribution of intellectual property. Infringements have become more prevalent and harder to trace with easier digital distribution mechanisms, insufficient storage security, and access control management.
Back in 2014, Sony Pictures was attacked by ‘Guardians of Peace’, a hacker group, that stole unreleased movie copies, scripts of future projects, and critical employee information. The hackers, who stole 100 terabytes of confidential data, demanded that Sony’s then much-anticipated release ‘The Interview’, a satirical take on Korean supremo Kim Jong Un, be stalled.
Popular streaming platforms such as Netflix, HBO, and Prime Video have now adhered to Google’s proprietary Widevine technology, a DRM standard, as a piracy prevention measure.
What is Information Rights Management?
Information Rights Management (IRM) involves the adoption of best data security practices such as encryption to prevent unauthorized access and is a subset of DRM. IRM implementation prevents users from unauthorized copying, deleting, printing, or downloading digital content. Advanced IRM tools can help administrators apply several additional data protection controls.
So how can Digital and Information Rights Management be implemented in a work environment? Parablu’s data protection technology helps you protect proprietary information effortlessly and cost-effectively.
Parablu’s Exclusive Digital and Information Rights Management Solution
Parablu’s BluSync™, a cloud-based content collaboration platform, has also proved to be an effective IRM solution. Tailored for secure collaboration, BluSync incurs no additional storage costs, can be easily managed through an intuitive interface, and has proved to be an ideal IRM option today.
- Secure File Transfer
Files transferred over conventional protocols offer no control over the recipient’s actions. BluSync allows secure file-sharing documents using password-protected URLs that would self-destruct after a defined period.
Multi-factor and brute force authentication as well as IRM techniques can be employed to prevent recipients from downloading, printing, as well as saving shared documents. BluSync’s anti-malware scanning feature helps mitigate possible threats arising from external collaboration.
- Policy-based Management
All file-sharing policies can be defined and managed through the BluSync console. Beyond the various encryption measures, BluSync also enables users to define email domains and geographical restrictions to prevent data tamper.
Policy-based management serves both IRM and DRM purposes since it restricts access to myriad kinds of shared data. For instance, defining the number of devices, people, and view limits could help mass media platforms. Whereas, defining editing, printing, and downloading file-sharing restrictions could greatly prevent malicious receiver actions.
- Zero-Knowledge Privacy
Built on the foundation of Zero-Knowledge Privacy, BluSync ensures nobody except authorized users can access the required information. This means neither Parablu, a cloud vendor, nor a foreign government.
“BluSync’s built-in IRM controls help prevent downloading, printing, as well as saving shared documents.”
- End-to-End Encryption
All shared files are encrypted by utilizing the industrial-strength AES-256 encryption standard. BluSync offers the data owners complete authority over their encryption keys, which eliminates dependency and trust in a cloud vendor over data security.
End-to-end encryption ensures both secure collaboration and prevention of unauthorized publishing of mass media forms such as movies, music files, and audiobooks.
- Identity Management
BluSync™ is engineered on the principle of zero trust and can be seamlessly integrated with identity management solutions such as Active Directory, Azure Active Directory, and Okta. The integration helps create exclusive namespaces for an authorized set of users.

Difference between Digital and Information Rights Management
So much said about DRM and IRM as well as the Parablu advantage, knowing the right context of their application may get confusing or overlap each other. The two terms are interrelated, and it is not only one or the other that needs to be addressed. While these two data protection approaches appear to be similar, several aspects clearly distinguish DRM and IRM.
- Nature of Data Protected
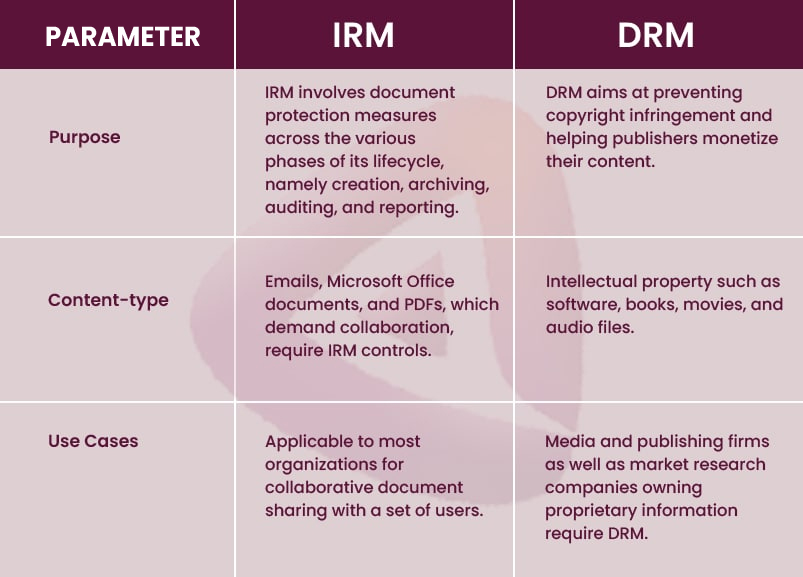
DRM applies to mass-produced audio and video files, whereas IRM restrictions are mostly imposed on documents such as spreadsheets, text files, and PowerPoint presentations. To elaborate, DRM aims to protect movies, audiobooks, and other common online-accessed media, whereas IRM controls ensure secure file sharing and document uploads/downloads across online forums.
- Document Protection and Monetization
DRM aims to protect owners of digital intellectual property to prevent copyright infringement and gain monetary benefits (such as increased subscriptions) over their published material. IRM is solely focused on the protection of documents such as Microsoft office files, emails, and PDFs from malicious activities. IRM is integral to various phases of the document life cycle such as creation, archiving, auditing, and reporting.
- Static Versus Highly Collaborative Information
DRM is relevant for static data already published in the public domain, which largely remains unchanged. IRM is recommended for documents frequently shared among a group of users, to ensure secure collaboration. While IRM allows the modification of documents, DRM rights are not transferable.
“While DRM applies to mass-produced audio and video files, IRM restrictions are mostly imposed on documents such as spreadsheets, text files, and PowerPoint presentations.”
DRM and IRM Use Cases
Are DRM and IRM a must-have for any digital enterprise? These use cases shed light on how DRM mitigates proprietary data management challenges across sectors and how your organization may adopt these. Similarly, it is also vital to understand how a correctly implemented IRM could prevent several data security challenges for an organization.
- Media & Publishing
Since the media & publishing industry relies on subscribers, being equipped with a DRM solution is imperative to prevent piracy incidents that render the subscriptions pointless. Unfortunately, readers would prefer to download a free pirated copy than pay extra to be a premium member.
By being equipped with a DRM solution, enterprises can impose different restrictions on their content usage.
- Active Directory Rights Management Services
Emails are hotbeds of malicious activity since transferring corrupted links and data tampering by receivers are commonplace. Recently, Microsoft initiated the Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS) to achieve IRM across Exchange Online accounts. The ADRMS enables the imposition of security permissions on emails directly to prevent malicious activity. These restrictions include preventing recipients from saving, printing, or downloading critical email information.
- Enterprise Digital Rights Management (EDRM)
EDRM falls within the purview of IRM since it involves data security. Enterprises rely on DRM to protect enterprise critical data such as design plans and Merger & Acquisition (M&A) preparations. A Gartner report has stated that Enterprise Digital Rights Management (EDRM) is estimated to be over $330 million by 2026. Imposing IRM controls over such confidential documents can significantly prevent data breach instances.
“A Gartner report has stated that Enterprise Digital Rights Management (EDRM) is estimated to be over $330 million by 2026.”
How does Information Rights Management (IRM) work?
IRM is the application of myriad data protection techniques to prevent malicious activity instances such as malware attacks and insider threats. All the measures can be implemented and centrally managed by an administrator.
- Defining Restrictions
Administrators can define access restrictions for different categories of users. These include restrictions on viewing, editing, and saving documents. In addition, unauthorized sharing of documents over emails can be prevented.
- Defining Access Periods
Making the shared information inaccessible after a defined period will reduce instances of data tamper.
- Encryption
Data encryption at the application level makes data accessible to only an authorized set of users. Encrypted documents help businesses significantly prevent tamper, especially when shared with an external set of users.
- Policy and Identity Certification
IRM also employs public-key cryptography for encryption and decrypts the document for the authentic receivers. The approach enforces access policies on documents that help individuals manage access permissions such as viewing and editing. These restrictions could also be modified remotely. IRM also generates a user identity certificate that mentions the document and furbishes other information useful from a file-sharing perspective.
- Identity Management
A subset of IRM is Identity Access Management (IAM) which allows an authorized set of users to access the right resources when required. IAM must be included in an enterprise’s data management strategy to comprehensively protect users, hardware, and software applications.
How BluSync™ Makes a Difference
BluSync™ stands out from conventional IRM enforcement methods in numerous ways. Primarily, the data protection measures can be easily managed from an interface that also helps an administrator comprehensively view the organizational data shared.
The product’s encryption approach also differentiates it from several IRM market variants, which implies users don’t have to trust cloud vendors completely with their data’s security. In addition, the product offers additional benefits such as litigation hold, and eDiscovery, differentiating it from several other market variants.
Learn more about BluSync™ and its benefits through a demo.









